我們的課程正在轉變 Our courses are changing
響應《生物多樣性策略及行動計劃》
推出更多生物多樣性相關課程,增進學生對環境保育及生物多樣性概念的認識
In response to the 《Hong Kong Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan》
More biodiversity-related courses are provided to enrich students’ knowledge in biodiversity conservation and sustainable development
課程內容與時並進
在不同的課題滲入STEM元素
To Keep abreast of modern educational development
The elements of STEM education are embedded in various courses.
更長的課程、更多元化的課題、更全面的學習
在農曆新年學校假期、復活節學校假期及七月初推行四日三夜及五日四夜課程。
Extended course time, more diversified topics and more comprehensive study
4-day/3-night and 5-day/4-night courses are conducted in Chinese New Year school holiday period , Easter school holiday period and early July.
生態歷奇專題活動帶出更深刻體驗
以最有趣味的生態現象激發學生思考,同時帶出課本內的生態學概念。
More profound experience acquired through Eco-adventure activities
Using the most interesting ecological phenomena to stimulate student to think, at the same time, to elucidate the ecology concepts in the textbooks.
將顯微觀察推向更高層次
計劃購置電子顯微鏡讓學生使用,將眼界帶往超乎想像的生物世界。
Towards another level of Microscopic observation
Planning to introduce Scanning Electronic Microscope, bringing the perspective to the biological world beyond imagination.
邁向全面電子化教學
所有考察課程,學生均獲發平板電腦輔助學習,平板電腦內置大量自行開發的生態考察學習材料。
Advancing towards comprehensive e-learning
Tablet computers installed with abundant self-developed ecology learning materials are provided in all the field study courses.
課程類別 Categories of course
傳統考察課程 (導引模式 / 探究模式)
Conventional field study courses (Instructional & Investigatory approach)
探究模式野外考察與導引模式野外考察的比較
Comparison of Investigatory field study and instructional field study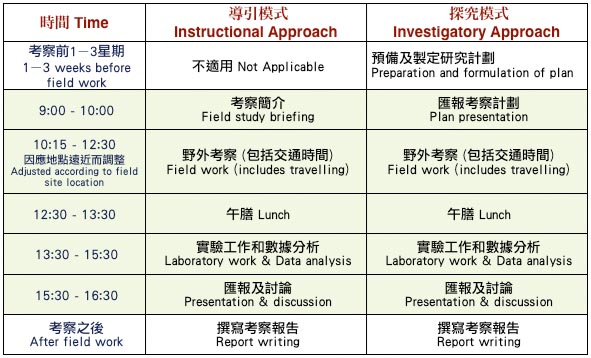
野外考察乃科學探究活動,過程包括觀察現象、提出問題、 擬訂假說、設計方法、進行實驗和詮釋結果。學生不但要從中驗證事物,還須掌握科學探究的過程,包括澄清問題、設計實驗、數據記錄和詮釋,以及將結果表達令人明白了解。在野外考察訓練的過程中,我們不單要求學生找到正確的答案,而且更培養學生在發展科學時須應用的技能。學生除了掌握事實和操作技巧外,還須學習成為具批判性的學習者。
Field study is a scientific investigation work which involve observing phenomena, defining problems, formulating hypotheses, designing and conducting investigations, and interpreting results. These kinds of activity are not only for verification purposes, but also allow students to understand the process of science, including how to clarify questions, how to design an experiment, how to record and interpret data, and how to communicate the knowledge generated. It should be noted that developing science process skills is as important as finding correct answers. Students are expected to master much more than facts and manipulative skills through field studies. They must learn to be critical thinkers.
課程目的 Course objectives
促使學生能夠
- 仔細觀察並提出適當的疑問、辨識問題關鍵所在及擬訂假設以作探究;
- 計畫和進行科學探究,並撰寫報告;
- 運用科學思維及具創造性
- 運用科學語言與他人有效地交流意見和觀點。
to enable students to :
- make careful observations, ask relevant questions, identify problems and formulate hypotheses for investigation;
- plan, conduct and write reports on scientific investigations;
- think scientifically and creatively;
- communicate ideas and views effectively with others, using the language of science.
學習經歷
- 仔細觀察並作出適當的提問、辨識問題關鍵所在及擬訂假說以作探究
- 計畫和進行科學探究,並撰寫報告
- 因應特定目的,選擇和設計合適的探究方法
- 運用適當的儀器和方法,進行實驗
- 辨識和解釋在科學探究中,控制變量的重要性
- 解釋在科學探究中,樣本量、隨機抽樣法、重覆實驗和步驟的重要性
- 分類、整理和展示直接和間接蒐集的數據
- 運用圖表、曲線圖、流程圖和模型表達從數據衍生出來的現象和關係
- 分析數據,並作出結論
- 了解科學探究的過程包括分析證據和提供以科學理論和概念為基礎的解說
- 利用邏輯和證據來擬訂及修正科學解說和模型
Learning experience
- make careful observations, ask relevant questions, identify problems and formulate hypotheses for investigations;
- plan, conduct and write reports on scientific investigations;
- select and design appropriate methods of investigations for specific purposes;
- use appropriate instruments and apply proper techniques for carrying out practical work;
- identify and explain the importance of control variables in scientific investigations;
- explain why sample size, random sampling, replicates and repeat procedures are important in scientific investigations;
- classify, collate and display both first and second hand data;
- use diagrams, graphs, flow charts and physical models as visual representations of phenomena and relationships arising from the data;
- analyse and draw conclusions from data;
- understand that the process of scientific investigations includes analyzing evidence and providing explanations based upon scientific theories and concepts;
- formulate and revise scientific explanations and models using logic and evidence.